Sectoral Analysis for Public Electricity Generation
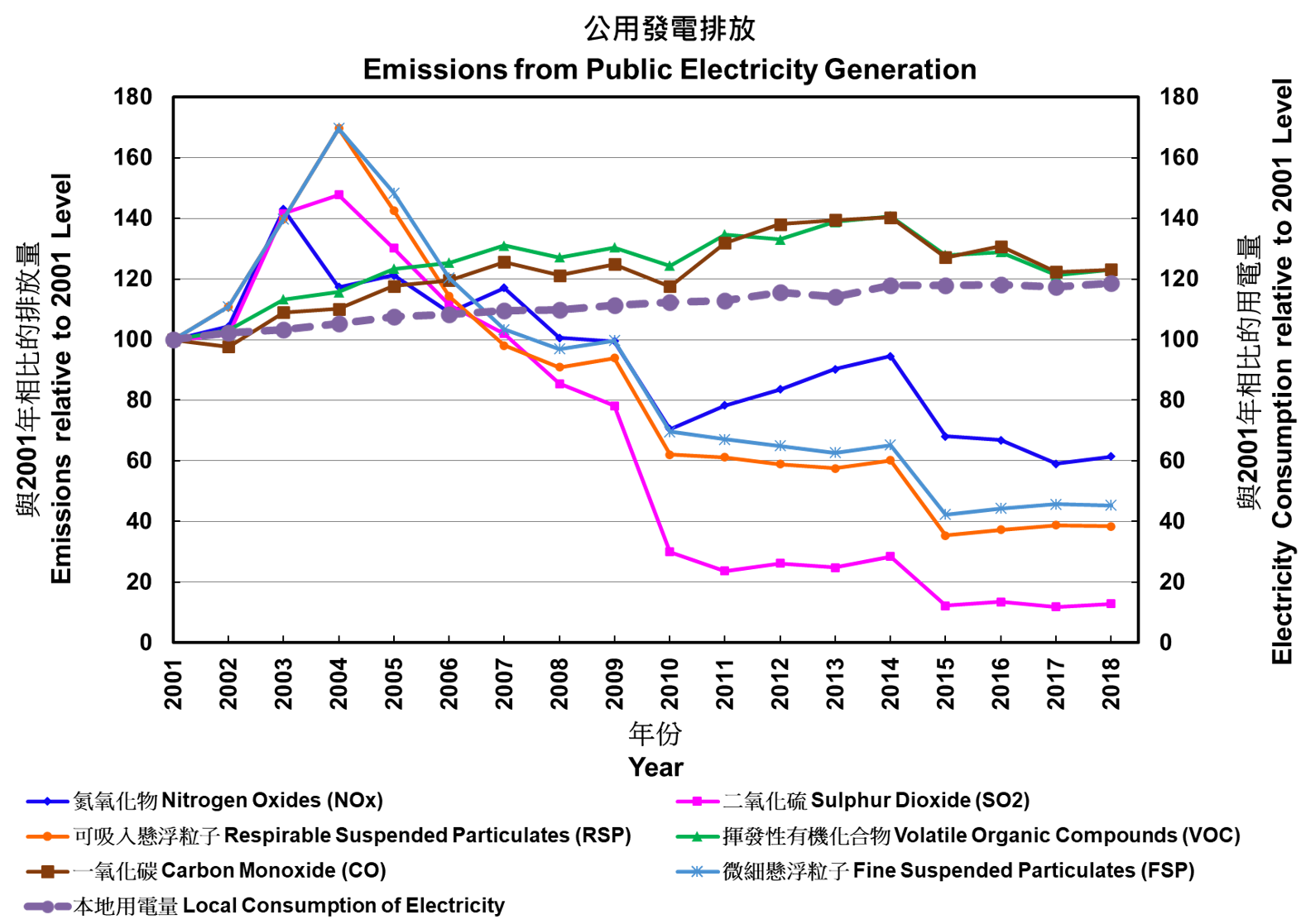
Electricity sector had been a major contributor to SO2, NOx and RSP emissions. Due to government’s continuous efforts to control emissions from the power sector, including the imposition of statutory emission caps on power plants, its SO2 emissions reduced substantially by 87%, NOx emissions by 39% and RSP emissions by 62% from 2001 to 2018, despite an increase in electricity consumption of 19%. In 2018, the emissions of SO2, NOx and RSP accounted for 47%, 28% and 16% of the total emissions, respectively.
The emissions of SO2, NOx and RSP from power sector continue to show a decreasing trend from 2010 to 2018, as power companies increased the use of natural gas for electricity generation in order to meet the emission caps on power plants set out in the Technical Memorandum (TM) for Allocation of Emission Allowances in respect of Specified Licences. The proportion of natural gas in the fuel mix would be increased to around 50% by 2020 and around 57% by 2024.
>The EPD has progressively tightened the emission caps since 2005. In 2008, we issued the first TM and stipulated emission caps for power plants for 2010 and beyond. So far, we have issued eight TMs and the last TM was issued in 2019 to further tighten the emission caps for 2024 and onwards. By 2024, the emission caps of SO2, NOx and RSP would be reduced by 87%, 71% and 69% respectively, as compared with the emission caps for 2010.