Sectoral Analysis for Navigation
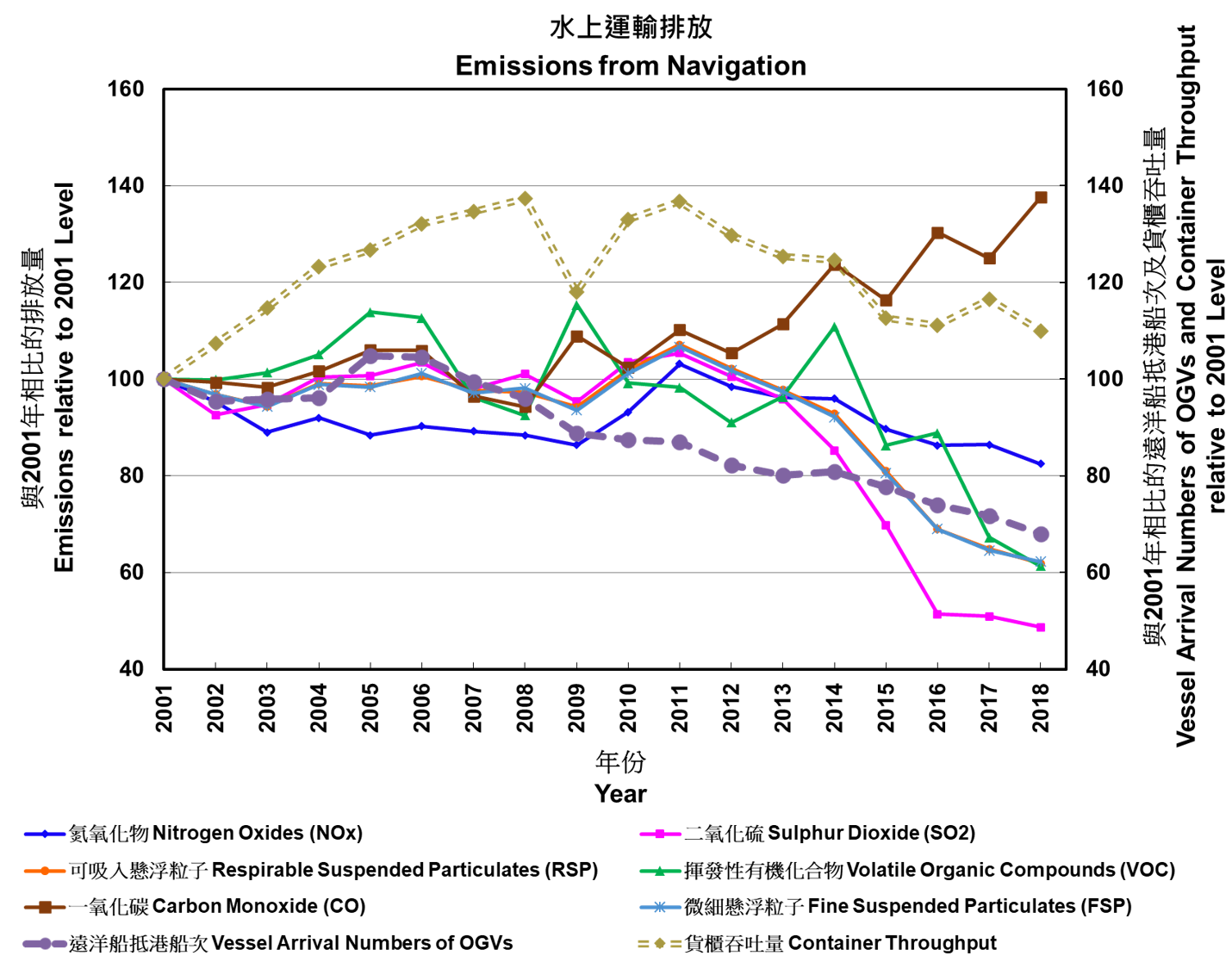
With the significant reduction in emissions from the electricity and road transport sectors over the past years, marine emissions have now become the major emission source in Hong Kong. Nonetheless, the emissions of SO2, RSP, FSP from vessels decreased substantially by 36% to 49% from 2013 to 2018. In 2018, the emissions of SO2, NOx, RSP and FSP from marine vessels accounted for 49%, 37%, 34% and 41% of the total emissions, respectively.
The reductions of SO2, RSP and FSP emissions from marine vessels from 2010 to 2018 were primarily achieved through marine control measures including the implementation of the Air Pollution Control (Marine Light Diesel) Regulation since April 2014 and the Air Pollution Control (Ocean Going Vessels) (Fuel at Berth) Regulation from July 2015 to December 2018. It is anticipated that emissions from marine vessels will be further reduced, as the Air Pollution Control (Fuel for Vessels) Regulation requiring all vessels to use compliant fuel, (including fuel with sulphur content not exceeding 0.5%), within the waters of Hong Kong was in force from January 2019.
Among vessels, ocean going vessels (OGVs) were the major emitters. As compared with 2010, the container throughput decreased by 17% in 2018, which also contributed to the reduction in emissions from marine vessels.