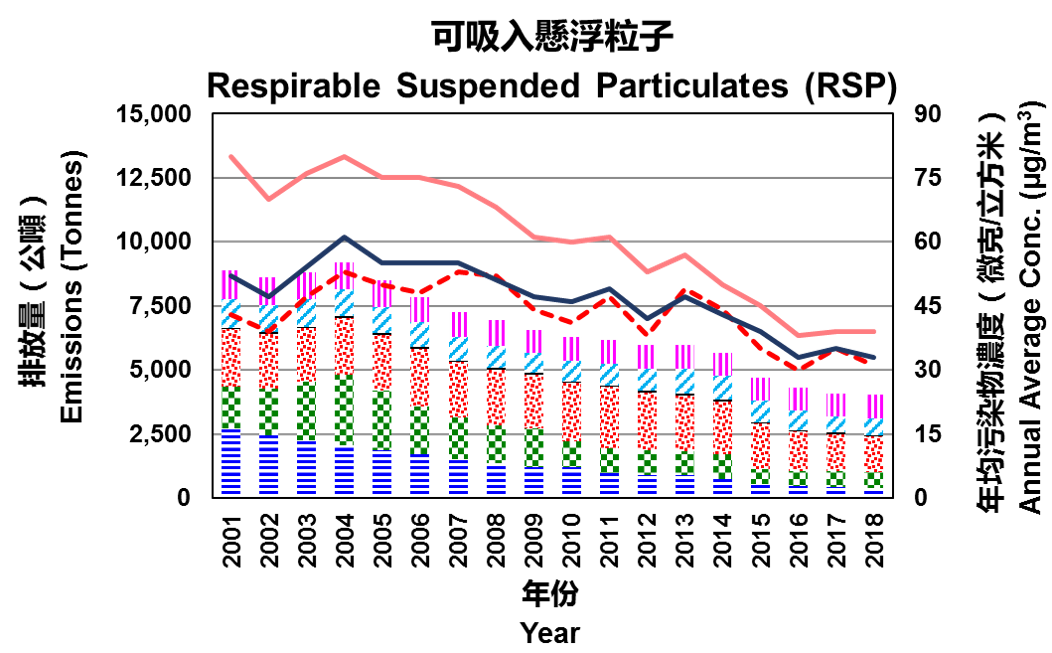

Between 2001 and 2018, RSP emissions decreased by 55% which were mainly caused by the decline in emissions from the road transport and public electricity generation sectors. Navigation and non-combustion sectors were the top two sources of RSP emissions, accounting for 34% and 23% of total RSP emissions in 2018, respectively.
The background RSP concentration levels measured at the Tap Mun air quality monitoring station over the years have been close to those measured at the general air quality monitoring stations, reflecting that RSP concentrations in Hong Kong are not only affected by local sources but also subject to strong regional influence. The gap between roadside and general (ambient) RSP concentration levels have been narrowing, indicating that vehicular emissions have been significantly reduced over the years.