Emergency Generator
Air Pollution
| Common Problems | Causes | Relevant Environmental Control |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive emission of dark smoke | Exhaust outlets locating too close to the nearby air sensitive receptors |
Under the Air Pollution Control (Smoke) Regulations, Cap. 311C, dark smoke emission from any chimney or relevant plant must not exceed 6 minutes in any period of 4 hours or 3 minutes continuously at any one time. Under the Air Pollution Control (Fuel Restriction) (Amendment ) Regulations, Cap. 311I, diesel fuel users in industrial and commercial sectors must now use ultra low sulphur diesel with a sulphur content of not more than 0.001% by weight. |
| Incomplete combustion of fuel | ||
| Inadequate air pollution control measures | ||
| Inadequate maintenance |
Practical Solutions
- Locate chimney at a dispersive area and away from domestic premises during design stage to avoid dark smoke during testing operation. Rooftop is becoming a popular choice due to its remoteness characteristic and better dispersion
- Select diesel generator type with high combustion efficiency to minimize dark smoke generation
- Avoid no load test which generated dark smoke from incomplete combustion
- Use existing building load for testing operation. Notify and agree with the affected occupants in advance
- Perform dummy load test to enhance complete combustion and minimize dark smoke generation
 |
|
|
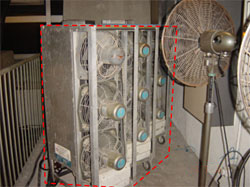
- Use fuel additives to improve combustion efficiency
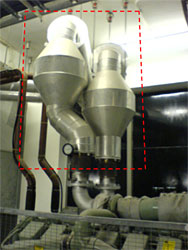
- Adopt catalytic after-treatment system, such as exhaust purifier, soot filter and particulate trap to reduce particulate emission and convert hazardous CO and HC to form CO2 & H2O
 |
|
|
- Conduct regular maintenance
Noise & Vibration Pollution
| Common Causes | Relevant Environmental Control |
|---|---|
| Too close to the nearby sensitive receivers | Under the Noise Control Ordinance, Cap. 400, noise caused by any emergency generator should not cause the noise level at Noise Sensitive Receivers (NSRs) to exceed the limit stipulated under the relevant Technical Memorandum. |
| Inadequate noise pollution control measures |
Practical Solutions
- Place the emergency generator in a plant room with thick walls, sound adsorption materials, sound proof door and silencers for air inlets/outlets
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
- Locate the plant room away from the nearby and future NSRs. Rooftop is becoming a good choice due to its remoteness
- Isolate the machine from the building structure by use of inertia blocks and vibration isolators
- Provide flexible connectors between the machine and associated pipework to avoid structural vibration transmission
- Use vibration isolators for attaching pipes to walls, ceilings or floors
- Make reference to the statutory noise limit and include noise levels specification when ordering new equipment
- Conduct regular maintenance, check alignment and replace worn-out components
- Seek professional advice from acoustic consultant/contractor
