Noise Criteria
Here are some commonly used terms when we refer to noise criteria.The term "Noise Sensitive Receiver", often abbreviated as NSR, refers to premises that is used for purposes sensitive to noise and requires protection. Examples of noise sensitive receivers are domestic premises, hotels and hostels, educational institutions and hospitals and clinics. Please click on the following diagram to see the enlarged photos.
Non-NSRs include multi-storey car parks and markets, godowns, community uses such as sports complexes and commercial centres or premises. Please click on the following diagram to see the enlarged photos.
A day is often divided into three time periods as indicated below :
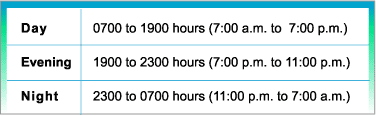
 Day |
 Evening |
 Night |
The Type of Area Containing NSR refers to the characteristics of the area in which the NSR is located. The table below indicates the types and contains some typical examples. There is a mimic photo for each of the examples. Click on the mimic photo for enlarged viewing.
The term "Influencing
Factors", abbreviated as IF, refers
to industrial areas, major roads or areas that are
situated within the boundary of the Hong Kong
International Airport. Their presence in the
vicinity of a NSR may dominate the ambient
or background noise there in such a way that
it is impractical to stipulate too low a noise
limit for either planning or control purpose.
The term "industrial area"
refers to an area which consists of a number
of factories or industrial establishments;
or an establishment which is having industrial
operation or operations of a significant scale.
A "major road" means a road
which has a heavy and generally continuous
flow of vehicular traffic and, in normal circumstances,
means a road with an annual average daily
traffic flow in excess of 30,000 vehicles. Where a
major road has an unusually low traffic flow
rate (less than 300 vehicles per hour) at
the time of day under consideration, it shall
not be considered as an IF at that time.
The term "Degree to which NSR is affected
by IF" refers to how the NSR is being
affected by the IF. It can be either :
- not affected, or
- indirectly affected, or
- directly affected.
For "directly
affected", the NSR is at such a position
that noise generated by the IF is readily
noticeable at the NSR and is a dominant feature
of the noise climate of the NSR.
"Indirectly affected" means
that the NSR is at such a location that noise
generated by the IF, whilst noticeable
at the NSR, is not a dominant feature of the
noise climate of the NSR.
For "not affected", the NSR
is at such a location that noise generated
by the IF is not noticeable at the NSR.
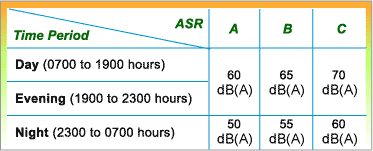
The "Area Sensitivity Rating",
abbreviated as ASR, is a rating of
the area in which the NSR is located. The
ASR can be either A, B or C and is derived
from the following table after knowing the
Type of Area Containing NSR,
any presence of IF, and "Degree
to which NSR is affected by IF".
Please click on the demo button to read the
details.
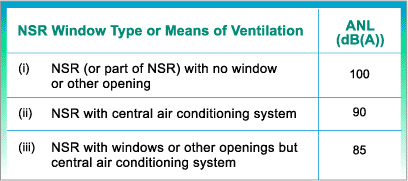
The ANLs shown in the above table are to be reduced by 10 dB(A) for NSRs such as hospitals, medical clinics, educational institutions, courts of law or other NSRs which are considered to be particularly sensitive to noise. Any associated noise measurement shall be made in Leq(5 min). For further details, please refer to the Technical Memorandum on Noise from Percussive Piling by clicking here. For details of the legislative control on percussive piling, please click here.
Demarcation of DAs can be viewed on the EPD website. For accessing it, please click here:
Some general construction work employ powered mechanical equipment (PME), i.e. machines driven by electricity, compressed air or hydraulic means. In other situations; the construction work may involve hammering and erection or dismantling of formwork or scaffolding.
Within Designated Areas, powered mechanical equipment (PME) is categorized into Specified Powered Mechanical Equipment (SPME) and non-SPME. The SPME are generally noisier and warrant tighter control.
The following are SPME:
- Hand-held breaker
- Bulldozer
- Concrete lorry mixer
- Dump truck
- Hand-held vibratory poker
- Erection or dismantling of formwork or scaffolding
- Loading, unloading or handling of rubble, wooden boards, steel bars, wood or scaffolding material
- Hammering
There are two sets of noise criteria or Basic Noise Levels, in dB(A), abbreviated as BNLs:
- BNLs contained in the Technical Memorandum on Noise from Construction Work in Designated Areas

The above
table is used in the assessment of CNP
applications for construction work using
one or more of the SPME in construction
sites located within DAs.
- BNLs contained in the Technical Memorandum on Noise from Construction Work other than Percussive Piling

This table is used in the assessment of CNP applications for construction work using any PME in construction sites located within Non-DAs; and for construction work using PME other than SPME in construction sites located within DAs.
The BNLs are modified to take into account the duration of the construction work and any CNPs hitherto issued for the same sites to give a set of Acceptable Noise Levels, abbreviated as ANLs. Any associated noise measurement shall be made in Leq(5 min). Noise from the construction sites is then predicted using standard acoustical principles. If the predicted noise does not exceed the ANLs, CNP will be issued. Otherwise, CNP will not be issued. For further details, please refer to the Technical Memorandum on Noise from Construction Work in Designated Areas and the Technical Memorandum on Noise from Construction Work other than Percussive Piling. For details of legislative control on general construction works other than percussive piling, please click here.
Apart from the above controls on construction activities under the Noise Control Ordinance, there are also noise criteria for carrying out daytime construction activities during the construction or decommissioning phase of designated projects under Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance. These noise criteria shall be met as far as practicable. All practicable mitigation measures shall be exhausted and the residual impacts minimized.

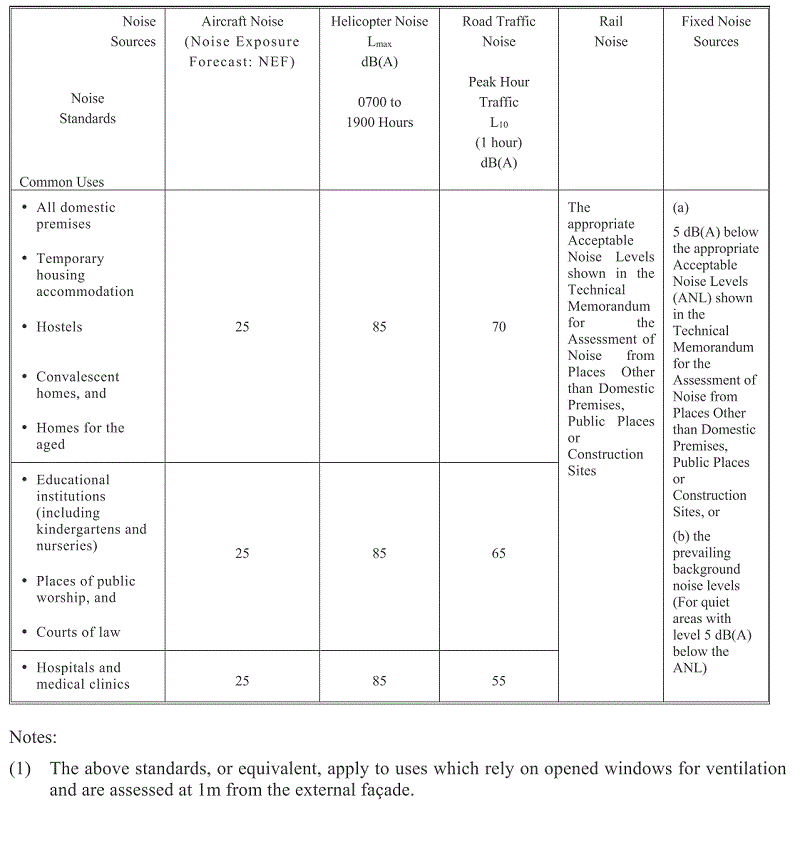
This kind of noise is controlled under a system of Noise Abatement Notices. The noise under investigation is measured and corrected for any special intrusive characteristics such as tonality, impulsiveness and intermittency in accordance with the Technical Memorandum for the Assessment of Noise from Places other than Domestic Premises, Public Places or Construction Sites issued under the Noise Control Ordinance(NCO).
If the noise is found to exceed statutory limits, a Noise Abatement Notice (NAN) will be issued to the relevant party or parties requiring them to abate the noise to within the statutory limits within a given time period. Table containing Acceptable Noise Levels (ANLs) in dB(A) of the Technical Memorandum is reproduced as follows :
The values in the above table apply to airborne noise. In case of noise transmitted primarily through the structural elements of a building or buildings, the appropriate ANL is 10 dB(A) less than the values shown in the table. This kind of noise is known as structural-borne noise. For examples, vibration from pumps and pipings may cause noise to be transmitted through the building structure.
The issue of ASR has been discussed in an earlier part of this Module. For a recap, please click here. The Technical Memorandum contains a special provision on ASR. The provision is as follows :
"Any NSR shall, irrespective of the above table, be assigned an ASR of C if it is within 100 m of a zone designated as Industrial or Industrial Estate on a statutory Outline Zoning Plan, or an ASR of B if it is between 100 m and 250 m from such a zone, except in cases where the above table indicates an ASR of C.For further details, please refer to the Technical Memorandum by clicking here.For details of legislative control on noise from places other than domestic premises, public places or construction site, please click here.
The principle is to ensure that:
- new noise sensitive uses are located where they will not be exposed to excessive noise levels;
- new noise emitters are located away from existing, committed or planned sensitive uses; and
- where
other constraints do not permit either of
the above, noise reduction designs should be incorporated into the noise
emitters at the earliest stage of planning. Where a completely acceptable
noise exposure cannot be obtained at the noise sensitive uses,
acoustic insulation should be provided.
For more details on mitigation measures, please click here.
The "Environmental Guidelines for Planning in Hong Kong", which form parts of the Hong Kong Planning Standards & Guidelines (HKPSG) published by the Planning Department, also provides guidelines on planning on most environmental issues.For further details on the Hong Kong Planning Standards & Guidelines (HKPSG), please click here and you will be directed to the website of the Planning Department.
















