Mitigation Measures
A noise barrier
or acoustic shield reduces noise by interrupting
the propagation of sound waves. With proper
design and selection of material for the noise barrier or
acoustic shield, noise reaching a noise sensitive
receiver would be primarily through diffraction over
the top of the barrier and around its ends.
The acoustical "shadow zone" created
behind the barrier is where noise levels are
substantially lowered.
To function well, the barrier must prevent the
line-of-sight between the noise source and the
receiver.
Effective noise barriers can reduce noise levels
by as much as 20 dB(A).
The following are some common types of noise
barriers used in Hong Kong.
Please click on the demo button to read the
details. Then click on the stop button to stop
the sound/demo.
The following table shows some examples of barriers erected in Hong Kong. Click on the mimic diagrams to see more details :
Noise Enclosure
To function well, a noise barrier must
prevent the line-of-sight between the noise
source and the receiver. This is not always
possible, especially with high-rise noise
sensitive uses. In this circumstance, noise
enclosures are required to provide appropriate
protection against environmental noise for
the noise sensitive uses.
In general, an enclosure can reduce noise
by more than 20 dB(A).
Similar to noise barriers, noise enclosure
should be designed to serve both acoustic
and aesthetic purposes.
The following are some common types of noise
barriers used in Hong Kong.
Please click on the demo button to read the
details. Then click on the stop button to
stop the sound/demo.
The following table shows some examples of enclosures erected in Hong Kong. Click on the mimic diagrams to see more details :
| Project | Characteristics | Mimic Photographs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Semi-enclosure for Tate's Cairn Tunnel Approach at Choi Hung Estate and Richland Gardens |
|
|
||||||||
| Full
Enclosure for Wong Chu Road |
|
|
||||||||

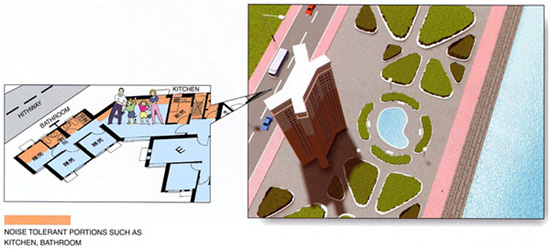
In such a design, the building is oriented so that less noise sensitive uses such as kitchen, bathroom and store rooms are located to one side of the flat while noise sensitive uses such as living rooms and bed rooms are located on the other side. The building is so oriented that the side of flat containing less noise sensitive uses is facing the major noise source such as a busy trunk road. This building arrangement can sometimes help to render sensitive development at an otherwise "environmentally unacceptable site" acceptable.
When traveling on level roads and at high-speed traffic, road/tyre interaction noise dominates. On inclined road or level at low-speed traffic, engine noise becomes dominant.
Most roads are paved with surface that has microscopic grooves which cause the noise to resonate, thereby increasing the noise. But a different material on the road will reduce the noise arising from road/tyre interaction.
Friction course, a special type of bituminous highway surfacing, was originally designed to improve skid resistance by virtue of its open texture. The open-textured bituminous highway surfacing consists of tiny holes making up 20% of the volume and can reduce traffic noise induced by the interaction between road surface and vehicles tyres of high-speed traffic by up to 5dB(A). Please click on the demo button to see the details.

The acoustic insulation will practically deprive the receivers of outdoor activities and an "open-window" life style. While acoustic insulation is commonly found in some western countries, the warm and humid climate in Hong Kong makes it more expensive for noise sensitive uses due to the need to provide air-conditioning for a "closed-window" environment.
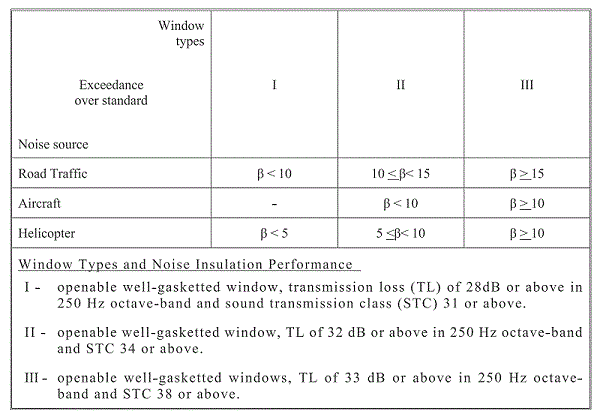
The suitable window types for noise insulation are shown in the following table. The table indicates the suitable window type that should be used when the estimated noise level will exceed the relevant standard by ß value.
A typical example of this measure is the School Insulation Programme. For details of this programme, please click here.








